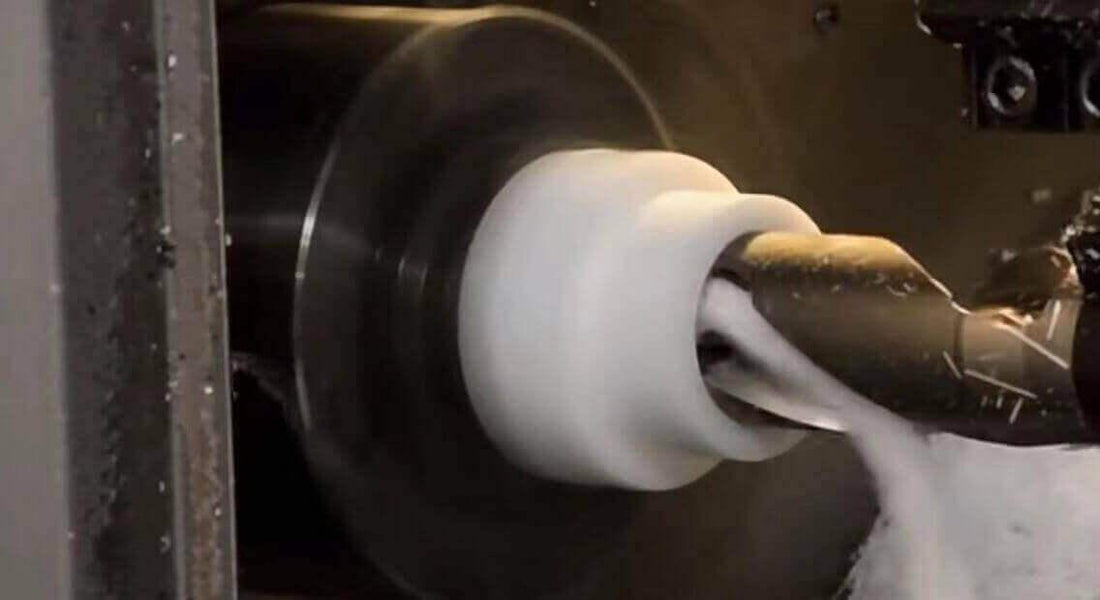
Polyoxymethylene (POM) custom processing, also known as acetal, polyacetal, or polyformaldehyde, is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic that is widely used in various industries and applications. It has excellent properties such as high stiffness, low friction, good dimensional stability, and resistance to wear, fatigue, and chemicals. POM can be classified into two types: homopolymer and copolymer, which have slightly different characteristics and performance.

However, joining and bonding POM parts with other materials is not a simple task. POM has poor adhesion to most substrates due to its low surface energy and high crystallinity. It also has a high coefficient of thermal expansion which can cause stress or deformation of the joint due to temperature changes. Moreover, POM may be incompatible with some materials or chemicals that can affect its quality or durability. Therefore, choosing the right joining method and avoiding the common bonding challenges of POM is crucial for achieving optimal results.
In this article, we will discuss the common joining methods and challenges of POM parts with other materials, and provide some tips and recommendations on how to join and bond POM parts effectively and efficiently.
Joining Methods
POM parts can be joined by various methods, depending on the desired strength, appearance, and function of the joint. Some of the most common joining methods for POM parts are:
- Adhesive bonding: This is a method for joining POM parts with other materials using an adhesive agent such as glue, epoxy, resin, etc. Adhesive bonding can provide a strong and durable joint with good aesthetics and flexibility. However, adhesive bonding requires proper surface preparation and treatment of POM parts to improve their adhesion. It also requires careful selection and application of the adhesive agent to ensure compatibility and curing.
- Welding: This is a method for joining POM parts with other materials using heat or pressure to melt and fuse them together. Welding can provide a strong and permanent joint with good mechanical properties and resistance to chemicals. However, welding requires special equipment and skills to perform safely and accurately. It also requires proper control of the welding parameters such as temperature, pressure, speed, time, etc. to prevent thermal degradation or distortion of POM parts.

- Mechanical fastening: This is a method for joining POM parts with other materials using mechanical devices such as screws, bolts, nuts, rivets, pins, etc. Mechanical fastening can provide a simple and fast joint with good adjustability and reversibility. However, mechanical fastening requires drilling or piercing of POM parts which can weaken their structure or cause stress cracking. It also requires proper selection and installation of the mechanical devices to ensure fit and function.
Bonding Challenges
While POM parts can be joined by various methods with other materials, it also poses some challenges and difficulties that need to be addressed during joining and bonding. Some of the main challenges and difficulties of joining and bonding POM parts with other materials are:Poor adhesion: POM has poor adhesion to most substrates due to its low surface energy and high crystallinity. This means that POM parts tend to repel rather than attract other materials or adhesives. Poor adhesion can result in weak or unstable joints that can fail under stress or load.
- Thermal expansion mismatch: POM has a high coefficient of thermal expansion which means it expands when heated and contracts when cooled. This can cause stress or deformation of the joint due to temperature changes. Thermal expansion mismatch can result in cracks or gaps in the joint that can compromise its strength or function.
- Chemical incompatibility: POM may be incompatible with some materials or chemicals that can affect its quality or durability. For example, POM may react with some acids or bases that can cause corrosion or degradation of POM parts. Chemical incompatibility can result in damage or failure of the joint due to chemical attack or leakage.
Solutions and Recommendations
To overcome or minimize the challenges and difficulties of joining and bonding POM parts with other materials, some solutions and recommendations are:
- Use proper surface preparation and treatment: The surface preparation and treatment of POM parts can improve their adhesion by increasing their surface energy or roughness. For example, POM parts can be cleaned with solvents or detergents to remove dirt or grease. They can also be etched with chemicals or plasma to create micro-pores or grooves on the surface. They can also be coated with primers or adhesion promoters to enhance their compatibility with other materials or adhesives.
- Use proper adhesive selection and application: The adhesive selection and application can ensure a strong and durable joint by matching the properties and performance of the adhesive agent with the POM parts and the other materials. For example, POM parts can be bonded with cyanoacrylate, epoxy, polyurethane, or acrylic adhesives that have good adhesion and curing characteristics. The adhesive agent should be applied in appropriate amounts and patterns to ensure uniform coverage and penetration. The adhesive agent should also be cured under controlled conditions and with proper equipment to ensure optimal bonding.

- Use proper welding parameters and techniques: The welding parameters and techniques can ensure a strong and permanent joint by controlling the heat and pressure applied to the POM parts and the other materials. For example, POM parts can be welded with ultrasonic, laser, hot plate, or spin welding methods that have suitable frequency, power, speed, time, etc. The welding parameters should be optimized to avoid overheating or underheating of POM parts, ensure uniform melting and fusion of POM parts and the other materials, prevent thermal degradation or distortion of POM parts, etc.
- Use proper mechanical fastening devices and methods: The mechanical fastening devices and methods can ensure a simple and fast joint by choosing the right size, shape, and type of the mechanical devices and installing them correctly on the POM parts and the other materials. For example, POM parts can be fastened with screws, bolts, nuts, rivets, pins, etc. that have suitable diameter, length, head, thread, etc. The mechanical devices should be selected and installed to ensure fit and function of the joint without causing damage or stress to POM parts.

POM is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic that can be joined and bonded with other materials by various methods to produce parts with excellent properties and versatile applications. However, joining and bonding POM parts with other materials also involves some challenges and difficulties that need to be addressed to achieve optimal results. By choosing the right joining method and avoiding the common bonding challenges of POM, you can join and bond POM parts effectively and efficiently.
We hope this article has given you some useful information and insights on how to join and bond POM parts with other materials. If you have any feedback or questions, please feel free to leave a comment below. We would love to hear from you.
You are interested in trying out POM material products or would like more information, please come and harass us. We'd love to be bothered by you and help you with your needs. Whether you need a free quote or any questions about the material or help with its use.
Our website: www.beeplastic.com
Click to contact: Polyoxymethylene (POM) custom processing